Apex action
The Apex action type allows you to execute a callable Apex class within a process. This action is highly flexible and enables advanced logic or integration with other Salesforce functionalities by invoking specific Apex methods.
Key Features
- Execute complex business logic using Apex code.
- Pass inputs dynamically to the Apex method.
- Retrieve outputs for use in subsequent process steps.
Configuring an Apex Action
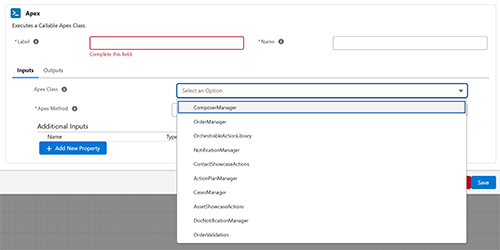
When adding an Apex action, you will see the following fields for configuration:
1. Common Properties
- Label:
- A user-friendly name for the action.
- Required field.
- Name:
- A unique identifier for the action, used internally.
- Required field.
2. Inputs
Inputs are the parameters passed to the Apex method. There are two types of inputs:
Predefined Inputs
- These are fields automatically determined by the action, such as:
- Apex Class: Select the Apex class that contains the method to execute. The system will show all the callable claseses in the org
- Apex Method: Specify the method within the selected class to call.
- You must fill these inputs correctly for the action to function.
- Both fields are mandatory.
Additional Inputs
- These are custom parameters you can define. Depends on the method you must to add the input fields for the method selected:
- Name: The identifier of the input parameter, which must match the parameter name expected by the Apex method.
- Type: The data type of the parameter (e.g., String, Number, Boolean).
- Value: The actual value or variable to pass to the Apex method.
Usage Example
Scenario: Sending a Custom Notification
- Apex Class:
accountHelperClass - Apex Method:
setAccountInactive - Additional Inputs:
- AccountId:
- Name: AccountId
- Type: String
- Value: {!recordId}
- NotificationMessage: The message to send.
- AccountId:
Best Practices
- Ensure the Apex method are properly configured to handle the inputs and return outputs.
- Always test the Apex method independently before integrating it into a process.