Billing Calculation Rules Definition
This process covers the definition of billing rules, determining how amounts are calculated based on various criteria.
Definition of Calculation Rules
Rules can define relationships with discounts, taxes, and dynamic tariff structures, ensuring accurate and compliant billing calculations.
Establishes calculation rules that determine billable amounts based on:
- Contracted products
- Applicable rates
- Contract terms
In Wattyo on Salesforce, these rules are configured in the billing module, allowing for no-code parameterization for ease of use.
Automatic validation rules can be applied before billing to prevent errors.
Rules can define relationships with discounts, taxes, and dynamic tariff structures, ensuring accurate and compliant billing calculations.
Every calculation rule must have a unique “Billable Concept” to be used in the billing process. This Billable Concept will be informed in every generated Invoice Line Item.
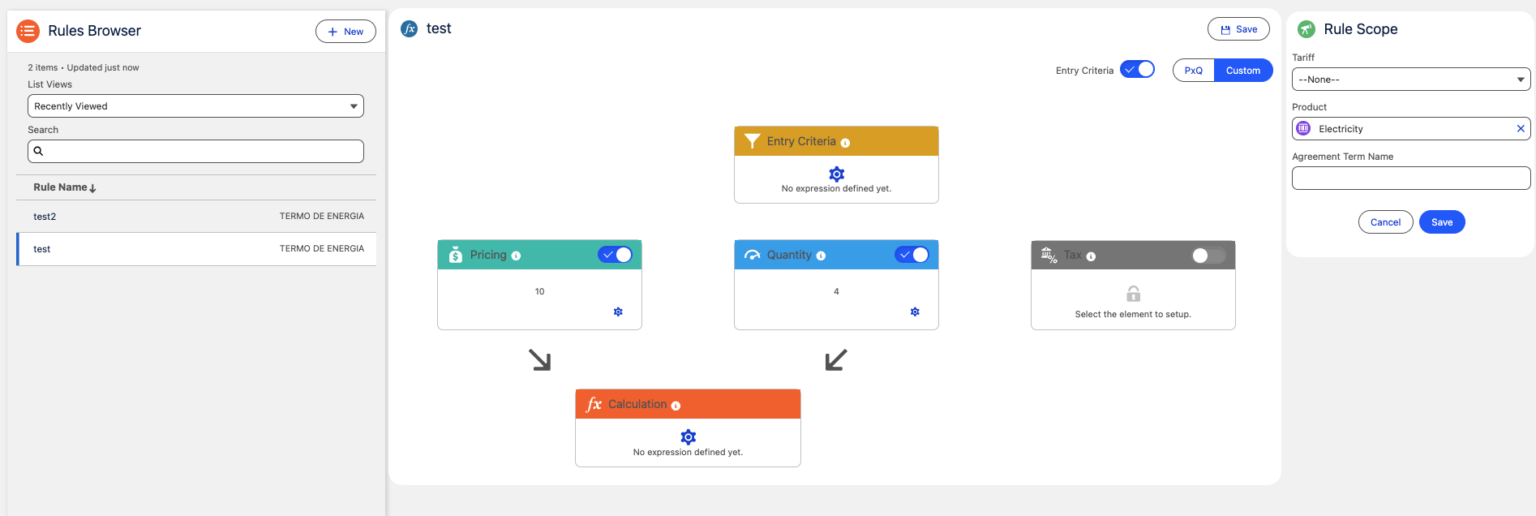
Rule Selection Criteria
The first filter to apply over Calculation Rules to decide if the rule applies to the current scenario is to use the selection Criteria.
The selection criteria can be based on:
- Contracted products: You can set “Product” on Calculation rule to apply only if a specific product is in the billable element (Order, Quote, Contract…).
- Tariff: You can set “Tariff” on Calculation rule to apply only if a specific tariff is in the billable element.
- Agreement Term: You can set “Agreement Term” on Calculation rule to apply only if a specific agreement term is included in the Agreement (Agreement as billable element).
Entry Rules
Additional filter to decide if the calculation rule apply on current scenario.
Once filtered the initial list using “Selection Criteria” the next step is to apply “Entry Rules” to filter the list of Calculation Rules to apply.
Entry Rules use Wattyo Rules Engine so you can apply more complex rules to filter the list of Calculation Rules.
For example you can configure a rule to be applied only if the $ConsumptionTotal is greater than 1000.
For more information, see the Billing Calculation Rules documentation.
Quantity Rules
Determines the quantity used for billing, based on:
- Recorded consumption
- Applicable periods
- Predefined value lists
Wattyo allows quantity rules to be applied through a value matrix, supporting complex calculations such as:
- Proportional allocations
- Time-based adjustments
Conditional rules can be applied to handle special data processing cases.
The OOTB Wattyo methods to process usage data use “Usage Blueprints” configuration to easy set the parameters needed to process the usage data.
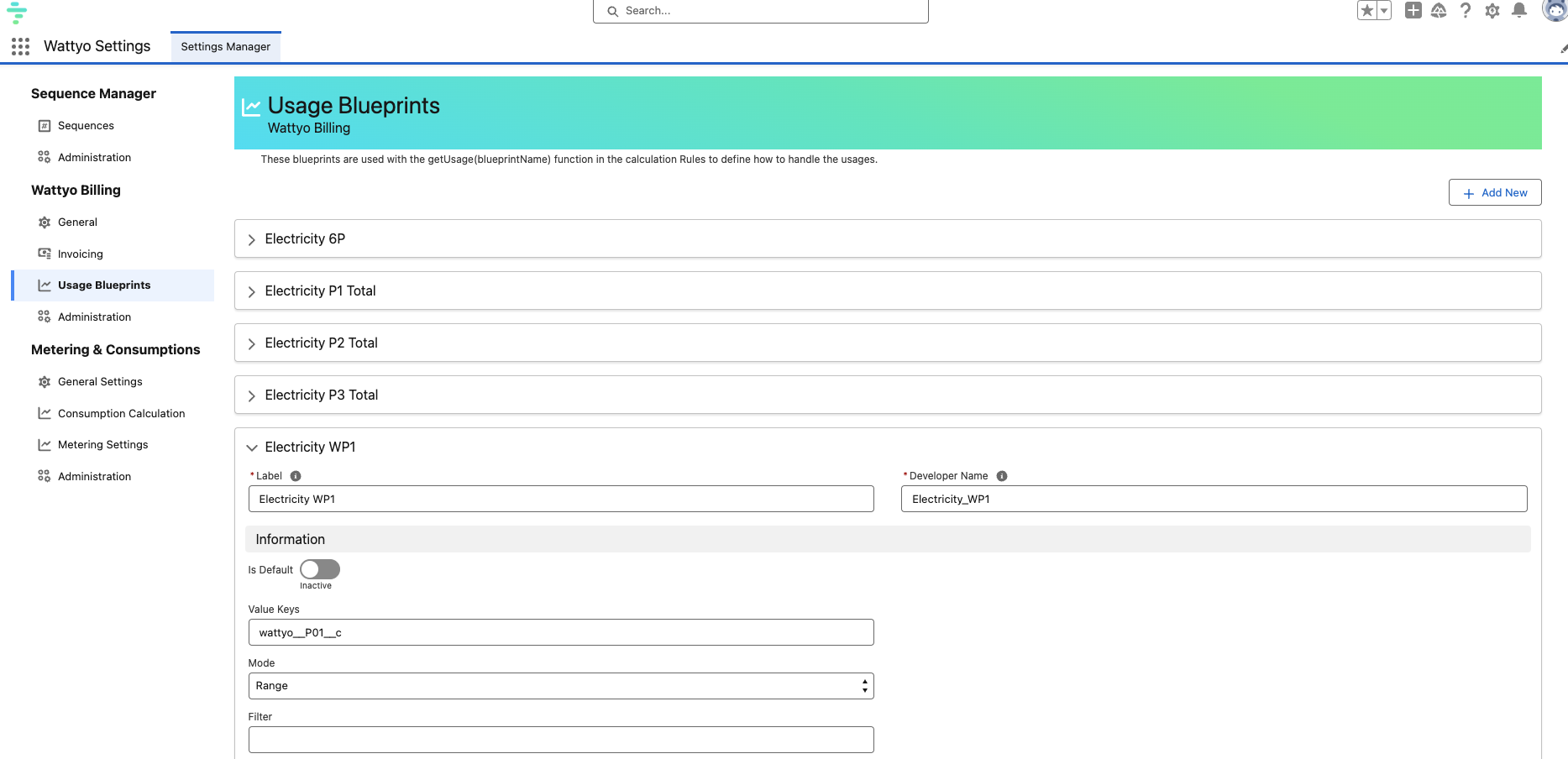
Note: The image shows the configuration of a Usage Blueprint in Wattyo, defining that only need to get the quantity in P01 field and without summing or average, we configured to get the full range to multiply against prices and apply exactly the right price on every period.
For more information, see the Usage for Billing documentation.
Pricing Rules
Defines how the price is determined for each billable item.
May include:
- Tiered pricing structures
- Adjustments based on time periods
- Indexation criteria application
In Salesforce, pricing rules are configured within the Pricing Rules objects and can be managed through dynamic interfaces.
The getPricing OOTB Wattyo method is used to get the price for a specific period and Billable Concept. It takes all the price field values but will only use the one that matches the usage.
You can configure pricing settings to get filtered prices (not only period and billable concept) and apply the right price to the right period.
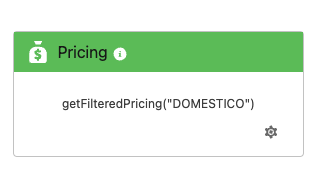
Note: The image shows the use of a Pricing Rule in Wattyo using Pricing Setting “DOMESTICO”.
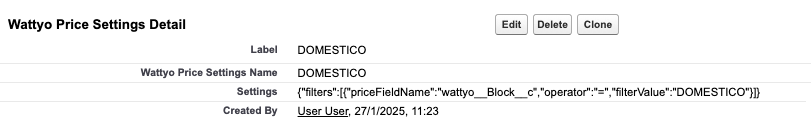
Note: The image shows the configuration of a Pricing Setting in Wattyo, defining that only need to get the prices with Block = DOMESTICO.
For more information, see the Billing Price Rules documentation.
Standard PxQ Operation
In Wattyo Billing, the default operation between Price and Quantity is PxQ, multiplying the price value (or list of values) by the quantity value (or list of values).

It’s important to remark that Price or Quantity could be a list (or a matrix with different price or quantity fields) so it’s posible to combine “Number x List”, “List x Number” or “List x List”.
Lists x Lists Adjustments
This operation requires the matching of quantity fields against price fiels to multiply the right values.
So you can have different fields only if the price is “Unique price” (flag).
The number of records in the list is not necessary to be the same because the calculation will be applied getting the right price for the quantity record period.
If quantity record period is greater than price record period, the calculation engine will split the consumption record to adjust to the price record limit (using prorating) price and try to locate the right price for the rest of consumption record.
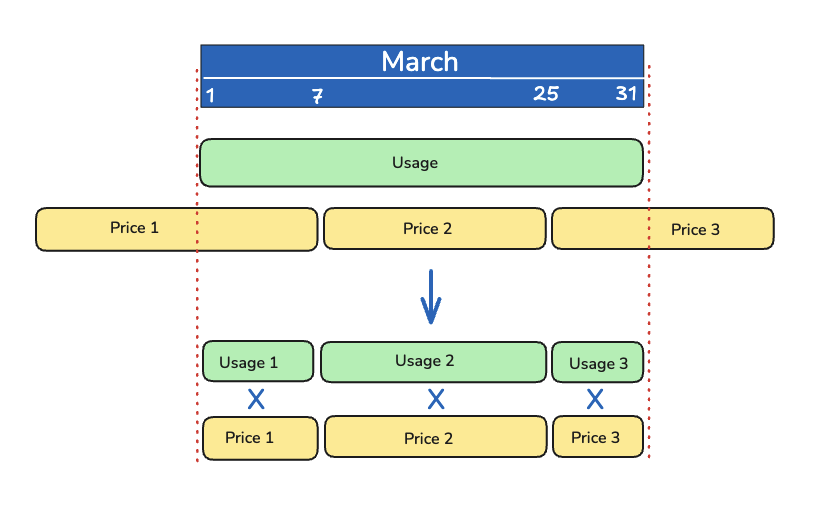
Note: The image shows how the calculation Enginge will apply the operation between different period size lists.
The result will be 3 different Invoice Line Items with the right price for each period.
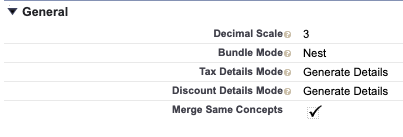
Is configuration is enabled (Merge same concepts) this spread should be merged into a single Invoice Line Item summing quantities and setting proportional avg price calculation.
Custom PxQ Operation
In Wattyo Billing, additional operations can be configured to model complex pricing rules, ensuring flexible and precise billing calculations.
The default operation between Price and Quantity is PxQ, multiplying the price value (or list of values) by the quantity value (or list of values).
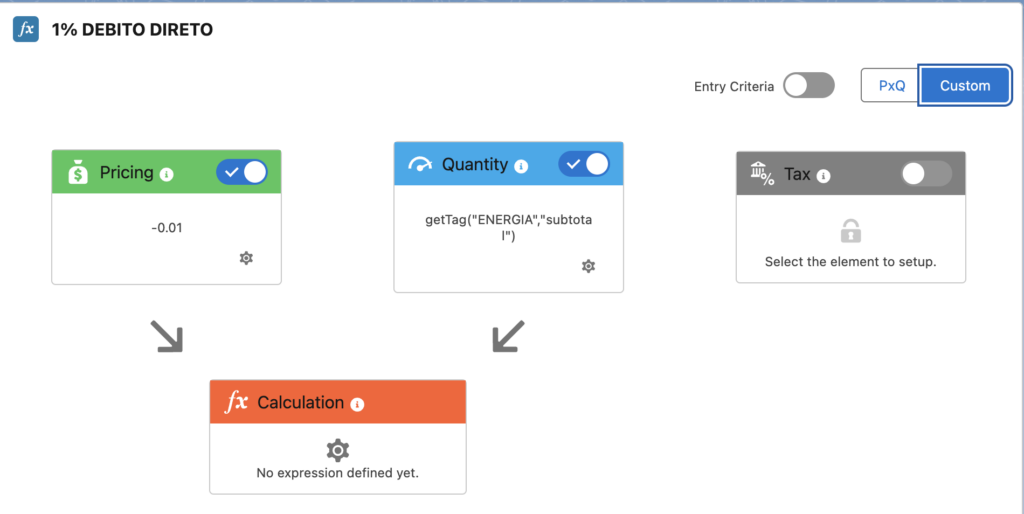
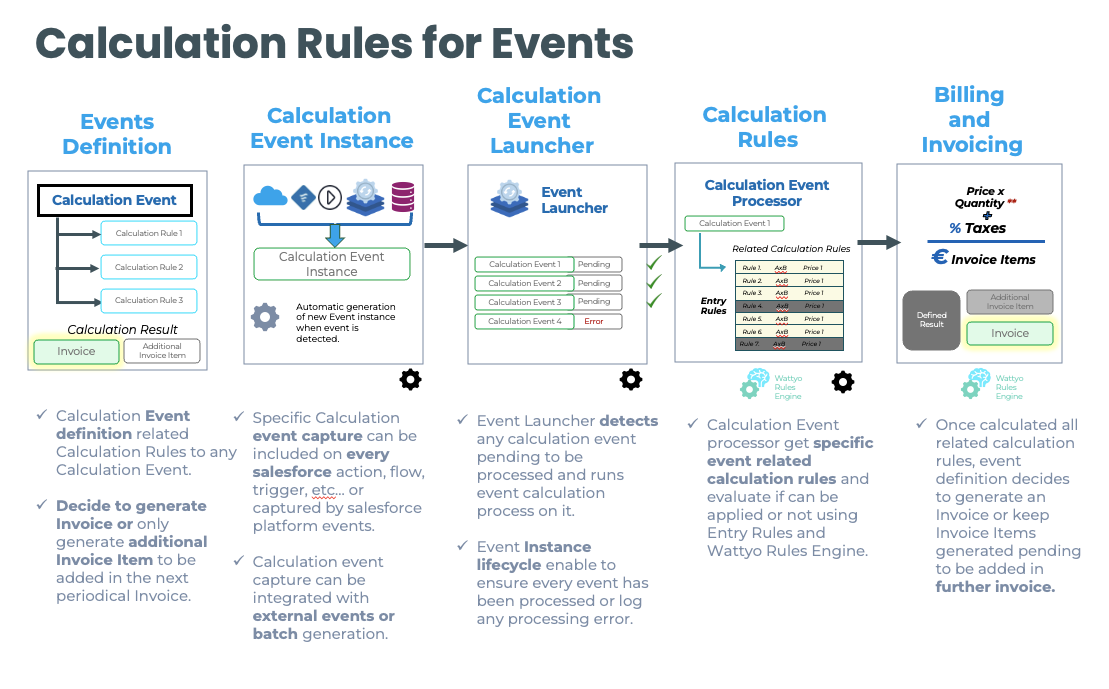
Calculation Rules for Events
In Wattyo Billing, specific Calculation Rules can be applied to events, allowing for the definition of specific rules for each event type.
It allows to define different rules for each event type, so you can have different rules for each event type.
Decide to generate Invoice or only generate additional Invoice Item to be added in the next periodical Invoice.